Description
| Games Are Important |
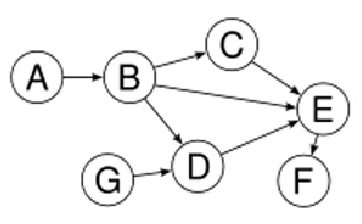
Suppose we have a directed acyclic graph with some number of stones at each node. Two players take turns moving a stone from any node to one of its neighbours, following a directed edge. The player that cannot move any stone loses the game. Note that multiple stones may occupy the same node at any given time.
The test case is terminated by n more integers
s0,..., sn-1 (one per line), where
si represents the number of stones that are initially placed on node
i ( 0![]() si
si![]() 1000).
1000).
Each test case is followed by a blank line, and input is terminated by a line containing `0 0' which should not be processed.
4 3 0 1 1 2 2 3 1 0 0 0 7 7 0 1 0 2 0 4 2 3 4 5 5 6 4 3 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
First Second 有一個DAG(有向五環(huán)圖),每個結點上都有一些石子。兩個玩家輪流把一個石頭從一個結點沿著從此點出發(fā)的任意一條有向邊移向相鄰結點。不能移動的玩家算輸?shù)粲螒颉W?意,在同一個時刻一個節(jié)點上可以有任意的石頭。 思路:注意到,各個石頭的狀態(tài)的是完全獨立的,所以這個游戲可以看做每個石頭所形成的游戲的和。對于每一個石頭,它的狀態(tài)x就是所在的結點編號,如果此結點已經(jīng)沒有出發(fā)的邊,則既是先手必敗的狀態(tài),否則后續(xù)狀態(tài)就是相鄰結點的SG值集合。需要注意的是,對于在同一個結點來說,其上的石頭如果個數(shù)為奇數(shù),則當成1個石頭即可;如果為偶數(shù),可以忽略不計。這是由異或運算的性質(zhì)決定的。
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> using namespace std; const int maxn = 10005; int n, m, sg[maxn]; vector<int> g[maxn]; int SG(int u) { if (sg[u] != -1) return sg[u]; int vis[maxn]; memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); for (int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); i++) { int tmp = SG(g[u][i]); vis[tmp] = 1; } for (int j = 0; ; j++) if (!vis[j]) { sg[u] = j; break; } return sg[u]; } int main() { int u, v; while (scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF && n+m) { memset(sg, -1, sizeof(sg)); for (int i = 0; i < maxn; i++) g[i].clear(); for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); g[u].push_back(v); } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) sg[i] = SG(i); int ans = 0, u; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { scanf("%d", &u); if (u & 1) ans ^= sg[i]; } printf("%s ", ans ? "First": "Second"); } return 0; }
