學習Java的同學注意了!!!
學習進程中遇到甚么問題或想獲得學習資源的話,歡迎加入Java學習交換群,群號碼:183993990 我們1起學Java!
今天1個偶然的機會我突然想看看JDK的動態代理,由于之前也知道1點,而且只是簡單的想測試1下使用,使用很快里就寫好了這么幾個接口和類:
接口類:UserService.java
1 package com.yixi.proxy; 2 3 public interface UserService { 4 5 public int save() ; 6 7 public void update(int id); 8 9 }
實現類:UserServiceImpl.java
1 package com.yixi.proxy; 2 3 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { 4 5 @Override 6 public int save() { 7 System.out.println("user save...."); 8 return 1; 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void update(int id) { 13 System.out.println("update a user " + id); 14 } 15 16 }
然后猴急猴急的就寫好了自己要的InvocationHandler:這個的功能是很簡單的就是記錄1下方法履行的開始時間和結束時間
TimeInvocationHandler.java
1 package com.yixi.proxy; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; 4 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 5 6 public class TimeInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { 7 8 @Override 9 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 10 throws Throwable { 11 System.out.println("startTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 12 Object obj = method.invoke(proxy, args); 13 System.out.println("endTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 14 return obj; 15 } 16 17 }
所有的準備工作都弄好了 固然要開始寫測試了!
Test.java
1 package com.yixi.proxy; 2 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; 3 4 public class Test { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 TimeInvocationHandler timeHandler = new TimeInvocationHandler(); 8 UserService u = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(UserServiceImpl.class.getClassLoader(), UserServiceImpl.class.getInterfaces(), timeHandler); 9 u.update(2); 10 u.save(); 11 } 12 }
愉快地Run了1下,不過它其實不給你面子 結果是滿屏幕的異常:
1 startTime : 1352877835040 2 startTime : 1352877835040 3 startTime : 1352877835040 4 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException 5 at $Proxy0.update(Unknown Source) 6 at com.yixi.proxy.Test.main(Test.java:11) 7 Caused by: java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException 8 at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) 9 at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:39) 10 at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25) 11 at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597) 12 at com.yixi.proxy.TimeInvocationHandler.invoke(TimeInvocationHandler.java:12) 13 ... 2 more
com.yixi.proxy.TimeInvocationHandler.invoke(TimeInvocationHandler.java:12)
異常明確告知了是在TimeInvocationHandle的12行的問題:也就是
1 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 2 throws Throwable { 3 System.out.println("startTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 4 Object obj = method.invoke(proxy, args); 5 System.out.println("endTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 6 return obj; 7 }
從方法上來看沒甚么毛病啊!由于在invoke()這個方法上貌似提供了method.invoke(Object,Object[])所要的所有的參數,我們會理所應當的去使用它,如果你真那樣想的話 那你就中了JDK的圈套了,先看下正確的寫法吧 避免有些同學沒心情看后面的 最少給個正確的解法:
修改TimeInvocationHandler.java
1 package com.yixi.proxy; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; 4 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 5 6 public class TimeInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { 7 8 private Object o; 9 10 public TimeInvocationHandler(Object o){ 11 this.o = o; 12 } 13 14 @Override 15 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 16 throws Throwable { 17 System.out.println("startTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 18 Object obj = method.invoke(o, args); 19 System.out.println("endTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 20 return obj; 21 } 22 23 }
修改Test.java
1 package com.yixi.proxy; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; 4 5 public class Test { 6 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 TimeInvocationHandler timeHandler = new TimeInvocationHandler(new UserServiceImpl()); 9 UserService u = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(UserServiceImpl.class.getClassLoader(), UserServiceImpl.class.getInterfaces(), timeHandler); 10 u.update(2); 11 u.save(); 12 } 13 }
現在是正確的輸出結果:
1 startTime : 1352879531334 2 update a user 2 3 endTime : 1352879531334 4 startTime : 1352879531334 5 user save.... 6 endTime : 1352879531335
如果想代碼少1點的話可以直接寫匿名類:
1 package com.yixi.proxy; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; 4 import java.lang.reflect.Method; 5 import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; 6 7 public class Test { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 final UserServiceImpl usi = new UserServiceImpl(); 11 UserService u = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance( 12 usi.getClass().getClassLoader(), 13 usi.getClass().getInterfaces(), 14 new InvocationHandler() { 15 16 @Override 17 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 18 throws Throwable { 19 System.out.println("startTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 20 Object obj = method.invoke(usi, args); 21 System.out.println("endTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 22 return obj; 23 } 24 }); 25 u.update(2); 26 u.save(); 27 } 28 }
既然method.invoke(target,args);中第1個參數是傳入的是目標對象 那末invocationHandler的Invoke方法要個Object proxy參數干嗎呢 ? 還是往下看吧!
對最重要的invoke這個方法(個人覺得)我們看下JDK是怎樣說的吧:
1 invoke 2 Object invoke(Object proxy, 3 Method method, 4 Object[] args) 5 throws Throwable在代理實例上處理方法調用并返回結果。在與方法關聯的代理實例上調用方法時,將在調用途理程序上調用此方法。 6 7 參數: 8 proxy - 在其上調用方法的代理實例 9 method - 對應于在代理實例上調用的接口方法的 Method 實例。Method 對象的聲明類將是在其中聲明方法的接口,該接口可以是代理類賴以繼承方法的代理接口的超接口。 10 args - 包括傳入代理實例上方法調用的參數值的對象數組,如果接口方法不使用參數,則為 null。基本類型的參數被包裝在適當基本包裝器類(如 java.lang.Integer 或 java.lang.Boolean)的實例中。
proxy - 在其上調用方法的代理實例 ? 這句話是甚么意思呢? 代理? method是代理的方法? 那我履行代理的method不是就應當是Object obj = method.invoke(proxy, args);嗎? 當時我也沒轉過彎來,去討論群,去google都沒找到甚么靈感,想一想還是這個看看源碼吧 或許能看到點甚么!
打開Proxy類的源碼發現有這么1個構造方法:
1 protected InvocationHandler h; 2 3 protected Proxy(InvocationHandler h) { 4 this.h = h; 5 }
把InvocationHandler作為Proxy的構造方法的參數....那它要InvocationHandler干甚么用呢?跟InvocationHandler中的invoke()方法有甚么聯系嗎?
我第1個想到的是Proxy內部會調用下面的語句:
1 h.invoke(this,this.getClass().getMethod(methodName),args);
由于總得去調用invoke方法才能履行相應的method方法吧,
我們先來看下這個
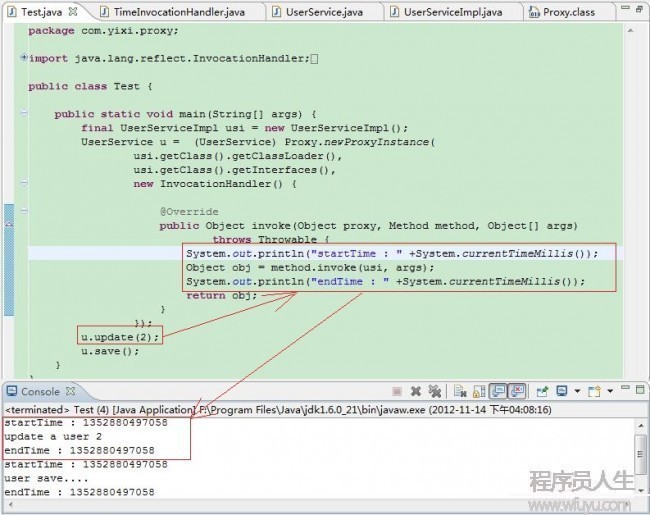
在這里你就會發現貌似有點感覺了:當u.update(2)時 Proxy就會調用 handler.invoke(proxyClass,update,2) 也就是調用了proxyClass.update(2);
當u.save();時 Proxy就會調用handler.invoke(proxyClass,save,null) 也就是調用了proxyClass.save();
所以1開始的毛病是對InvocationHandler的invoke方法的理解的毛病! 全部的invoke()方法
1 @Override 2 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 3 throws Throwable { 4 System.out.println("startTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 5 Object obj = method.invoke(usi, args); 6 System.out.println("endTime : " +System.currentTimeMillis()); 7 return obj; 8 }
其實就是代理對象的1個代理方法,履行代理對象的1個方法就會訪問1次invoke()方法;在invoke方法中的Object obj = method.invoke(usi, args); 是按原對象本應當履行的方式履行,該返回甚么就返回甚么。不知道你能想到點甚么啵。下面來驗證1下:
當Test.java改成這樣時:
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 final UserServiceImpl usi = new UserServiceImpl(); 5 UserService u = (UserService) Proxy.newProxyInstance( 6 usi.getClass().getClassLoader(), 7 usi.getClass().getInterfaces(), 8 new InvocationHandler() { 9 10 @Override 11 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) 12 throws Throwable { 13 return null; 14 } 15 }); 16 u.update(2); 17 u.save(); 18 } 19 }
注意這時候候的匿名類的方法的返回的是null,運行1下就會發現:
1 Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException 2 at $Proxy0.save(Unknown Source) 3 at com.yixi.proxy.Test.main(Test.java:17)
17行有空指針 也就是這里的u.save()方法有為null的元素 難道是u是空的? 不應當啊如果u是null的話那末u.update(2)在那里就會報空指針異常了,當我把17行注釋掉以后異常沒了說明u.update()能正常履行。那這究竟是為何呢?
其實這就是invoke方法返回null的原因:
注意1下UserService類中的兩個方法:
1 public interface UserService { 2 3 public int save() ; 4 5 public void update(int id); 6 7 }
Save()方法返回的是int型的 而update方法返回的是void型的;根據上面的猜想是 handler.invoke()是實現 proxyClass.update(2);的,invoke方法中的return方法的是相應的代理方法的返回值,
所以在invoke方法返回null的時候代理的update方法接收到返回值是null, 而它本來就是返回void 所以沒有報異常, 而代理save必須返回int型的數值 我們這返回的還是null,JVM沒法將null轉化為int型 所以就報了異常了
這樣解釋就可以解釋通了,也能相對證明前面的猜想。
InvocationHandler中invoke方法中第1個參數proxy貌似只是為了讓Proxy類能給自己的InvocationHandler對象的援用調用方法時能傳入代理對象proxyClass的援用,來完成proxyClass需要完成的業務。
學習Java的同學注意了!!!
學習進程中遇到甚么問題或想獲得學習資源的話,歡迎加入Java學習交換群,群號碼:183993990 我們1起學Java!
