大數據處理算法三:分而治之/hash映射 + hash統計 + 堆/快速/歸并排序
來源:程序員人生 發布時間:2015-07-03 08:38:36 閱讀次數:4582次
百度面試題1、海量日志數據,提取出某日訪問百度次數最多的那個IP。
IP 是32位的,最多有個2^32個IP。一樣可以采取映照的方法,比如模1000,把全部大文件映照為1000個小文件,再找出每一個小文中出現頻率最大的 IP(可以采取hash_map進行頻率統計,然后再找出頻率最大的幾個)及相應的頻率。然后再在這1000個最大的IP中,找出那個頻率最大的IP,即 為所求。
百度面試題2、搜索引擎會通過日志文件把用戶每次檢索使用的所有檢索串都記錄下來,每一個查詢串的長度為1⑵55字節。
假定目前有1千萬個記錄(這些查詢串的重復度比較高,雖然總數是1千萬,但如果除去重復后,不超過3百萬個。1個查詢串的重復度越高,說明查詢它的用戶越多,也就是越熱門。),請你統計最熱門的10個查詢串,要求使用的內存不能超過1G。
第 1步借用hash統計進行預處理: 先對這批海量數據預處理(保護1個Key為Query字串,Value為該Query出現次數,即Hashmap(Query,Value),每次讀取1 個Query,如果該字串不在Table中,那末加入該字串,并且將Value值設為1;如果該字串在Table中,那末將該字串的計數加1便可。終究我 們在O(N)(N為1千萬,由于要遍歷全部數組1遍才能統計處每一個query出現的次數)的時間復雜度內用Hash表完成了統計;
第2步借用堆排序找出最熱門的10個查詢串:時間復雜度為N'*logK。保護1個K(該題目中是10)大小的小根堆,然后遍歷3百萬個Query,分別和根元素進行對照(對照value的值),找出10個value值最大的query
終究的時間復雜度是:O(N) + N'*O(logK),(N為1000萬,N’為300萬)
或:采取trie樹,關鍵字域存該查詢串出現的次數,沒有出現為0。最后用10個元素的最小推來對出現頻率進行排序。
我們先看HashMap 實現
1. HashMap的數據結構
數據結構中有數組和鏈表來實現對數據的存儲,但這二者基本上是兩個極端。
數組
數組存儲區間是連續的,占用內存嚴重,故空間復雜的很大。但數組的2分查找時間復雜度小,為O(1);數組的特點是:尋址容易,插入和刪除困難;
鏈表
鏈表存儲區間離散,占用內存比較寬松,故空間復雜度很小,但時間復雜度很大,達O(N)。鏈表的特點是:尋址困難,插入和刪除容易。
哈希表
那末我們能不能綜合二者的特性,做出1種尋址容易,插入刪除也容易的數據結構?答案是肯定的,這就是我們要提起的哈希表。哈希表((Hash table)既滿足了數據的查找方便,同時不占用太多的內容空間,使用也10分方便。
哈希表有多種不同的實現方法,我接下來解釋的是最經常使用的1種方法―― 拉鏈法,我們可以理解為“鏈表的數組”
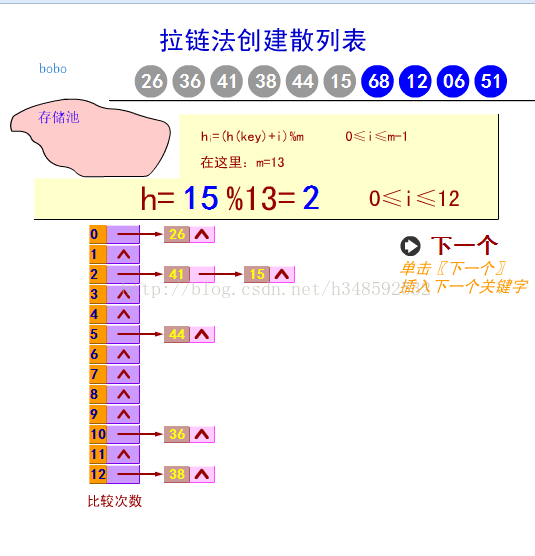
我用java 自己實現了1個HashMap,固然這比較簡點,不過能說明大概原理,改有的功能基本上有了
index=hashCode(key)=key%16
哈希算法很多,下面我用了java自帶的,固然你也能夠用別的
/**
* 自定義 HashMap
* @author JYC506
*
* @param <K>
* @param <V>
*/
public class HashMap<K, V> {
private static final int CAPACTITY = 16;
transient Entry<K, V>[] table = null;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public HashMap() {
super();
table = new Entry[CAPACTITY];
}
/* 哈希算法 */
private final int toHashCode(Object obj) {
int h = 0;
if (obj instanceof String) {
return StringHash.toHashCode((String) obj);
}
h ^= obj.hashCode();
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
/*放入hashMap*/
public void put(K key, V value) {
int hashCode = this.toHashCode(key);
int index = hashCode % CAPACTITY;
if (table[index] == null) {
table[index] = new Entry<K, V>(key, value, hashCode);
} else {
for (Entry<K, V> entry = table[index]; entry != null; entry = entry.nextEntry) {
if (entry.hashCode == hashCode && (entry.key == key || key.equals(entry.key))) {
entry.value = value;
return;
}
}
Entry<K, V> entry2 = table[index];
Entry<K, V> entry3 = new Entry<K, V>(key, value, hashCode);
entry3.nextEntry = entry2;
table[index] = entry3;
}
}
/*獲得值*/
public V get(K key) {
int hashCode = this.toHashCode(key);
int index = hashCode % CAPACTITY;
if (table[index] == null) {
return null;
} else {
for (Entry<K, V> entry = table[index]; entry != null; entry = entry.nextEntry) {
if (entry.hashCode == hashCode && (entry.key == key || key.equals(entry.key))) {
return entry.value;
}
}
return null;
}
}
/*刪除*/
public void remove(K key){
int hashCode = this.toHashCode(key);
int index = hashCode % CAPACTITY;
if (table[index] == null) {
return ;
} else {
Entry<K, V> parent=null;
for (Entry<K, V> entry = table[index]; entry != null; entry = entry.nextEntry) {
if (entry.hashCode == hashCode && (entry.key == key || key.equals(entry.key))) {
if(parent!=null){
parent.nextEntry=entry.nextEntry;
entry=null;
return ;
}
}
parent=entry;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> map=new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("1", "2");
map.put("1", "3");
map.put("3", "哈哈哈");
System.out.println(map.get("1"));
System.out.println(map.get("3"));
map.remove("1");
System.out.println(map.get("1"));
}
}
class Entry<K, V> {
K key;
V value;
int hashCode;
Entry<K, V> nextEntry;
public Entry(K key, V value, int hashCode) {
super();
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.hashCode = hashCode;
}
}
/* 字符串hash算法 */
class StringHash {
public static final int toHashCode(String str) {
/* 我用java自帶的 */
return str.hashCode();
}
}
生活不易,碼農辛苦
如果您覺得本網站對您的學習有所幫助,可以手機掃描二維碼進行捐贈


