|
1
|
MagicNumber -> autoresizingMask -> autolayout |
以上是純手寫(xiě)代碼所經(jīng)歷的關(guān)于頁(yè)面布局的3個(gè)時(shí)期
在iphone1-iphone3gs時(shí)期 window的size固定為(320,480) 我們只需要簡(jiǎn)單計(jì)算1下相對(duì)位置就行了
在iphone4-iphone4s時(shí)期 蘋(píng)果推出了retina屏 但是給了碼農(nóng)們非常大的福利:window的size不變
在iphone5-iphone5s時(shí)期 window的size變了(320,568) 這時(shí)候autoresizingMask派上了用處(為啥這時(shí)候候不用Autolayout? 由于還要支持ios5唄) 簡(jiǎn)單的適配1下便可
在iphone6+時(shí)期 window的width也產(chǎn)生了變化(相對(duì)5和5s的屏幕比例沒(méi)有變化) 終究是時(shí)候拋棄autoresizingMask改用autolayout了(不用支持ios5了 相對(duì)屏幕適配的多樣性來(lái)講autoresizingMask也已過(guò)時(shí)了)
那如何快速的上手autolayout呢? 說(shuō)實(shí)話 當(dāng)年ios6推出的同時(shí)新增了autolayout的特性 我看了1下官方文檔和demo 就立馬拋棄到1邊了 由于實(shí)在過(guò)于的繁瑣和啰嗦(有過(guò)經(jīng)驗(yàn)的朋友肯定有同感)
直到iPhone6發(fā)布以后 我知道使用autolayout勢(shì)在必行了 這時(shí)候想起了之前在閱讀Github看到過(guò)的1個(gè)第3方庫(kù)Masonry 在花了幾個(gè)小時(shí)的研究使用后 我就將autolayout掌握了(重點(diǎn)是我并沒(méi)有學(xué)習(xí)任何的官方文檔或其他的關(guān)于autolayout的知識(shí)) 這就是我為何要寫(xiě)下這篇文章來(lái)推薦它的緣由.
介紹
Masonry 源碼:https://github.com/Masonry/Masonry
Masonry是1個(gè)輕量級(jí)的布局框架 具有自己的描寫(xiě)語(yǔ)法 采取更優(yōu)雅的鏈?zhǔn)秸Z(yǔ)法封裝自動(dòng)布局 簡(jiǎn)潔明了 并具有高可讀性 而且同時(shí)支持 iOS 和 Max OS X。
我們先來(lái)看1段官方的sample code來(lái)認(rèn)識(shí)1下Masonry
|
1
2
3
|
[view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) { make.edges.equalTo(superview).with.insets(padding);}]; |
看到block里面的那句話: make edges equalTo superview with insets
通過(guò)鏈?zhǔn)降淖匀徽Z(yǔ)言 就把view1給autolayout好了 是否是簡(jiǎn)單易懂?
使用
看1下Masonry支持哪1些屬性
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *left;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *top;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *right;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *bottom;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *leading;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *trailing;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *width;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *height;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *centerX;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *centerY;@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) MASConstraint *baseline; |
這些屬性與NSLayoutAttrubute的對(duì)比表以下
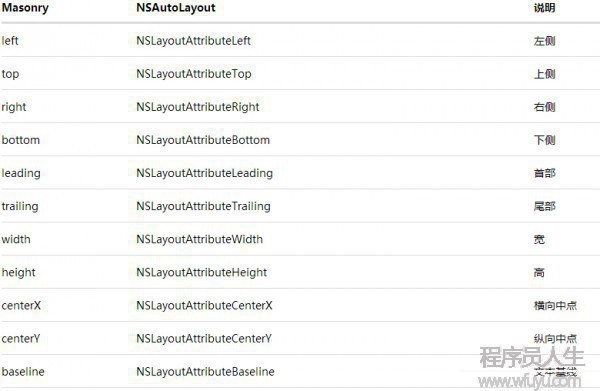
其中l(wèi)eading與left trailing與right 在正常情況下是等價(jià)的 但是當(dāng)1些布局是從右至左時(shí)(比如阿拉伯文?沒(méi)有類似的經(jīng)驗(yàn)) 則會(huì)對(duì)調(diào) 換句話說(shuō)就是基本可以不理不用 用left和right就行了
在ios8發(fā)布后 又新增了1堆奇奇怪怪的屬性(有興趣的朋友可以去瞅瞅) Masonry暫時(shí)還不支持(不過(guò)你要支持ios6,ios7 就沒(méi)必要去管那末多了)
在講實(shí)例之前 先介紹1個(gè)MACRO
|
1
|
#define WS(weakSelf) __weak __typeof(&*self)weakSelf = self; |
快速的定義1個(gè)weakSelf 固然是用于block里面啦 下面進(jìn)入正題(為了方便 我們測(cè)試的superView都是1個(gè)size為(300,300)的UIView)
下面 通過(guò)1些簡(jiǎn)單的實(shí)例來(lái)簡(jiǎn)單介紹如何輕松愉快的使用Masonry:
1. [基礎(chǔ)] 居中顯示1個(gè)view
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|

下一篇 什么才算是真正的編程能力?